SuZhou Ribo life science Ltd. Co. and Ribocure Pharmaceuticals AB (Ribo) presented four key scientific findings at the 2025 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress, underscoring significant progress in siRNA-based cardiovascular therapeutics pipeline.
Ribo presented results from its ApoC3-silencing RBD5044 program`s Phase 1 clinical trial, which included single and multiple ascending dose studies (n=72 healthy subjects). A single injection led to a substantial reduction of ApoC3 of up to 84% accompanied by a triglyceride (TG) reduction of up to 70 %, that remained below 50% of baseline at 6 months follow-up. In addition, participants showed an overall improved lipid profile with markedly reduced remnant cholesterol (up to 70%) and ApoB (up to 20 %) and a profound increase in HDL (up to 40%). The drug was well-tolerated, with no dose-dependent adverse events or liver enzyme elevations at the highest dose tested. Taken together, the safety and efficacy data position this ApoC3 siRNA as a potential best-in-class asset.
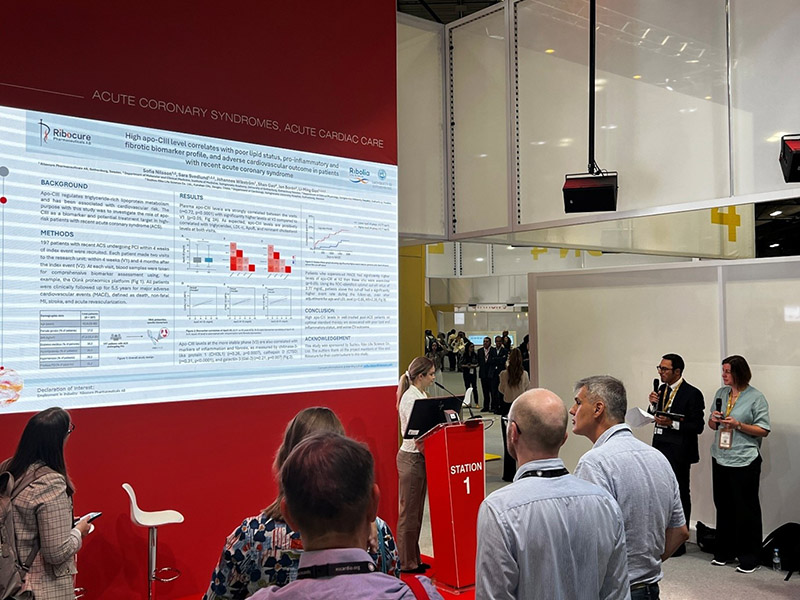
These interventional data were complemented by a clinical observational study, exploring the role of ApoC3 in 197 high-risk patients following acute coronary syndrome on top of optimal standard of care. As expected, elevated ApoC3 was linked to an unfavourable lipid profile. More importantly, ApoC3 levels were positively associated with proinflammatory and profibrotic biomarkers. During a 5.5-year follow-up, patients with high ApoC3 had a >2-fold increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Together with the interventional findings, these results support a causal role of ApoC3 in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and at the same time indicate its potential role in systemic inflammation, as well as potential for outcome benefit upon silencing in this population.
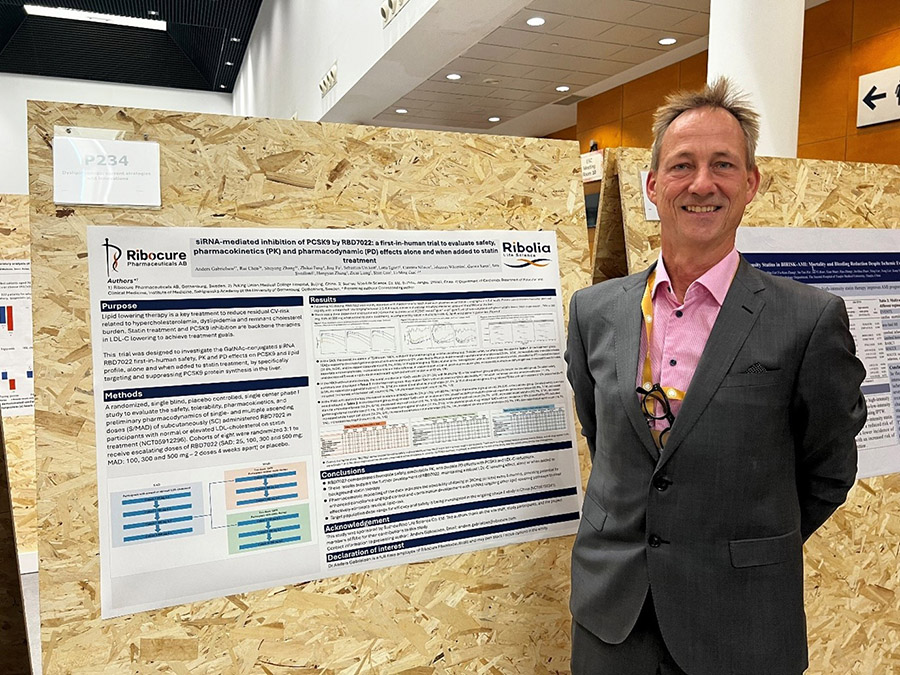
Ribo also presented Phase 1 data on its PCSK9 program RBD7022, now in Phase 2, with enrolment completed. The study included both healthy volunteers and hypercholesterolemic patients on background statin treatment. Using PCSK9 levels as a marker of target engagement, in patients with and without statin background therapy, the administration of RBD7022 demonstrated a maximal reduction of up to 75%, maintaining this level of suppression at 6 months follow-up. The treatment was well-tolerated, and the results strongly support continued development of this program as a key component of the LDL-lowering therapeutic arsenal.
Finally, Ribo highlighted its FXI siRNA program RBD4059, the world’s first and most advanced in clinical development, currently in Phase 2. Using deep-phenotyping data in high-risk coronary artery disease patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, Ribo showed that high FXI levels were associated with elevated endothelial activation biomarkers and impaired endothelial function during follow-up after the index event. These observational findings suggest that FXI silencing may deliver important pleiotropic benefits beyond its potent antithrombotic effect, offering protection with minimal bleeding risk.
Collectively, these presentations at ESC 2025 highlight Ribo’s commitment to advancing siRNA-based cardiovascular medicines, with multiple programs showing promise in addressing unmet needs in lipid management and thrombosis. Further updates are anticipated as clinical development progresses.